アクラマン
| ラテン表記 | Acraman |
| 緯経度 | 南緯 32°01′ (-32.02°) / 東経 135°27′ (+135.45°) |
| 国/地域 | オーストラリア |
| 州/地方 | サウス・オーストラリア州 |
| 直径 | 160 km; ∼90 km (NASA); 55 km (PASSC) |
| 年代 | ∼590 Ma |
アクラマン・クレーターは、G. Williamsが1986年に発見し、‹サイエンス›で報告した。また、このクレーターの形成で飛び散ったエジェクタ層がフリンダース山地で発見され、同じ号で発表された。
アクラマン・クレーターの中心部は低地になっており、雨期にはアクラマン湖(Lake Acraman)となる。衝突の証拠が発見された露頭へは、湖沼の中を歩いて渡らなくてはならない。
アクラマン・クレーター。
中央の丸い湖が、クレーター中央のアクラマン湖で、その周りを円環状に湖群が囲んでいる。最大の湖は、アクラマン湖の北東にあるゲアドナー湖(Lake Gairdner)。
右下の水面はスペンサー湾、左下の水面はグレート・オーストラリア湾。(図2の地図を参照)。
衛星: STS‐51‐A スペース・シャトル〈ディスカヴァリー〉
センサー: カメラ
日付: 1994‐11‐08/16
|
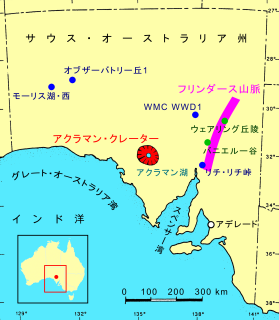
アクラマン・クレーターの周辺の地図。
青い円●はエジェクタ、緑の円●はスフェルールの発見地。
|
画像準備中 露頭の観察へ向かう1991年オーストラリア・クレーター巡検のメンバー。
|
画像準備中 衝突堆積物層の上下の地層。白い層の中に衝突堆積物層がある。
|
画像準備中 衝突堆積物層。中央の褐色層が衝突堆積物層。
|
文献
Gostin, VA; Haines, PW; Jenkins, RF; Compston, W; Williams, IS. 1986. Impact ejecta horizon within Late Precambrian shales, Adelaide geosycline, South Australia. Science, 233, 198–200.
Wallace, MW; Gostin, VA; Keays, RR. 1990. Spherules and shard‐like clasts from the late Proterozoic Acraman impact ejecta horizon, South Australia. Meteoritics, 25, 161–165.
Williams, GE. 1986. The Acraman impact structure: source of ejecta in late Precambrian shales, South Australia. Science, 233, 200–203.